What is SIP trunking? What is trunk- Sip Trunking Vs. VOIP?
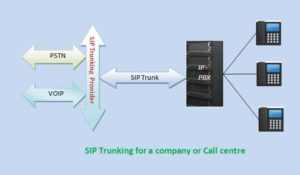
SIP trunking is a newer and more convenient means of communication using VOIP for a high concurrent call volume. A PBX connects to a SIP trunking provider over the Internet. The IP phones connect to the PBX for receiving and sending calls outside the office premises.
Almost every industry requires a large call volume for business. Sip trunking is the technology that enables VoIP for business.
With SIP trunking, one can have a cost-effective, scalable, and convenient alternative for existing PSTN/ISDN lines.
Sip Trunking
Almost every industry requires a large call volume for business. Sip trunking is the technology that enables VoIP for business. With SIP trunking, one can have a cost-effective, scalable, and convenient alternative for existing PSTN/ISDN lines.
SIP trunking has two parts one is SIP protocol, and the other is trunking. To explain better, we will explain each component in detail.
What is Session Initiation Protocol(SIP)?
SIP is a signaling protocol for establishing, modifying, and terminating a media session over the IP network. A media session can be for voice, video, fax, etc. There are two types of channels/paths in communication. One is a signaling channel, and the other is a media or voice path. SIP is a signaling protocol to set up a media session, and other protocols, e.g., GTP, carries media frames.
For setup, a session, sip protocol messages carry media endpoint information in session description protocol (SDP) as payload. The primary endpoint information is the IP address and port.
When you dial a number from a SIP phone, a session is established. After that, the phone does a voice sampling and converts it into network protocol messages.
SIP Uses the service of underlying TCP/IP or UDP/IP.
What is the trunk in telecom?
A trunk is a widespread term in telecom. You may have heard about it in the olden days. A long-distance call was called a trunk call.
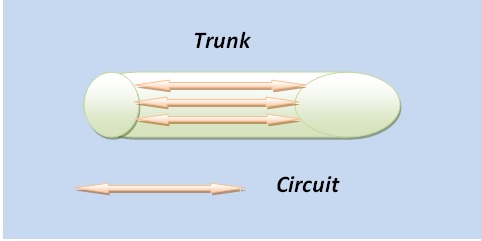
A group of communication lines is a trunk. Many callers or agents can share lines. For example, all customers dial the same customer support number to talk to agents. But at the same time, multiple customers can be served. Because for each call, a line is allocated from the trunk. The telephone line in our home for PSTN is a trunk with one line only.
Each communication line in the group is called a circuit. PSTN uses the ISUP protocol for Signaling. In ISUP, each line is a circuit identified by a circuit identification code (CIC) with dedicated bandwidth. A CIC is marked busy when there is an incoming or outgoing call. PSTN uses SS7 for the transport of ISUP Signaling over a network. In SS7, a trunk can have a maximum of 31 or 24 channels. Few are for Signaling, and the remaining for voice or media.
The SIP trunk has no physical limit on the number of lines. But concurrent calls can be limited by the underlying IP network bandwidth or from the SIP trunk provider. Based on the above, SIP trunking is a logical connection a VoIP company provides for making multiple concurrent calls over IP networks. An example is the IP PBX of a company. It connects to the trunking over SIP and internally to the phones called extensions.
How Sip trunking works :
The work is based on VoIP call concepts. If someone or a company wants to use the SIP Trunk, he has to purchase the account details from a service provider for the SIP trunk parameters. A company should have a PBX if the PBX is not supporting IP calls (not an IP PBX). Then PBX needs to upgrade for the VOIP feature.
The next step is to configure trunking connection details in the IP PBX.
Now call from an extension to the external phone number. IP-PBX does the SIP signaling with the trunk provider. As a result, VOIP call is set up with an external phone number. The external phone number may be a VoIP, PSTN, or mobile phone. If not a VoIP number, then there will be a conversion from VoIP to PSTN. You do not need to worry about this conversion. The trunking provider takes care of all the necessary transformations.
VOIP and Sip Trunking:
From the name, it looks that only the SIP protocol is sufficient. But it is not the case. SIP alone can do only signaling. For a complete call, other VoIP technologies work together. This includes the streaming of media over an IP network.
Sip trunking vs. PRI:
The first question that comes here what is PRI? We all have seen traditional phone lines coming to our office or home. These lines are called the Primary Rate Interface (PRI) lines. A wire connects to the handset on one end, and another connects to a telephone box. Following is a comparison of PRI lines with the SIP lines in tabular form.
| SIP Trunk | PRI Lines |
| Relatively new. | Old and traditional lines. |
| No specialized hardware is required. Ethernet or WiFi connectivity is only necessary for the SIP trunk. | Special hardware is required. The equipment is a PRI card. The system using the card also needs to install the software or driver for the card. |
| There is no type. All connections use the same IP lines for communications. There are no limitations on channels. | A PRI line can be of T1 or E1 type. T1 has 24 channels, and E1 has 31 channels. The maximum bandwidth for T1 is 1.544 Mbps and for E1 2.048 Mbps, respectively. |
| Same IP network. There is nothing like voice and data channels. | Signaling and actual voice data flow on separate channels. |
| Bandwidth is not guaranteed. Speed depends on underlying IP network speed. | Bandwidth is guaranteed. |
| Low cost and need no dedicated lines. | High in cost and need to maintain separate lines. |
| Easy to scale when concurrent calls increase. | Not easy, as scaling requires adding more physical lines. |
| SIP trunk providers can provide redundancy by rerouting traffic in the case of failure to another SIP server for VoIP calls. | Only a single switching center connects to the PRI line, and calls can not reroute, so they are not redundant. |
Sip trunking providers:
There are many sip trunking providers. Which provider is suitable for you depends on your requirements. Here is the list of many sip trunking providers.
Sip trunking pricing:
We have discussed sip trunking and its benefits for business. Now the next thing comes, how much does this cost? The answer is not as simple. The trunking cost depends on many factors. Few are listed here.
Setup Fee: Initially, moving to new providers needs to set up connections. This may take some significant time. The user might not be an expert in technical stuff for setup VOIP. This may lead to hiring an expert, or the sip trunking company will set up and charge an amount.
Concurrent Calls: Capacity is always a significant factor in deciding the cost. SIP trunking comes with the advantage of pay as the business grows. Initially, sip trunk users may purchase a simple plan and then can opt for a bigger plan in the future as volume increases. Change in the plan does not require any additional cost on any equipment.
Current PBX: If a company is using IP-PBX, then no cost is required for using SIP trunking. But if there is no PBX or no IP-PBX. This adds additional software in sip trunking pricing. Either PBX needs to upgrade to VoIP or purchase a new IP-PBX. Their option may be a cloud-based hosted IP PBX or an in-house installed solution.
VoIP Numbers: If a business already has a number, then the number needs to be ported on VoIP. Else a new number will be purchased. The option chosen will impact the sip trunking pricing.
Sip Trunking for business:
Business needs the advantages of flexibility and cost. With VOIP, no limit on channels as PRI lines have. A company can choose an option on a usage basis. You can pay a minimum for only one channel; on needs, one can pay for 1000 channels.