What is the HLR and VLR lookup? How to get MCC and MNC?
The HLR lookup refers to retrieving a mobile subscriber’s status and other information from telecome network. A lookup application must send a request message over SS7 to the Home Location Register (HLR) with a mobile number (MSISDN). It’s also known as a reverse phone number lookup. An MSISDN, or Mobile Station International Subscriber Directory Number, is a sequence of digits that make up a mobile number.
A successful lookup response includes status, roaming, and subscriber main identity. The visiting MSC, status (Active or Inactive), and subscribe information (IMSI) are all included in the roaming details.
IMSI is static information representing a subscriber’s global identity, whereas MSC number is dynamic information that changes as a subscriber moves from one location to another. Because the MSC number has a country code and an area code, visiting MSC provides an approximate location of a subscriber. An operator assigns each geographical location an area code.
How can we get Mobile Number Portability(MNP) information from HLR Lookup?
To drive number portability (MNP) status, we can use IMSI and MSISDN. The number is not ported if the IMSI and MSISDN belong to the same mobile operator. Otherwise, it is ported.
What are the Network Nodes involved in HLR lookup?
BTS (2G): A Base Transceiver Station is an element of a GSM network with an antenna for wireless communication with mobile devices. When a mobile phone is turned on, the BTS is the first node that is contacted. A cell is a small area that a BTS covers. A single BTS can cover a large number of cells.
BSC(2G): The base Station Controller controls the BTS and allocates the radio resources for a Mobile device. A BSC handles the handovers between cells. The connection between BTS and BSC is a wired connection. A single BSC controls multiple BTS.
MSC in Telecom: Mobile Switching Center is the node that bridges a wireless network to the rest of the PSTN. It holds the location, does billing, and does handovers between BSCs. An MSC implements roaming/ messaging and the call control protocol.
VLR: Visitor Location Register is the database in the roaming network. Which is mainly co-located with an MSC. It maintains location and other services in the roaming network. When a subscriber moves to a new VLR, HLR removes the subscriber information from the previous VLR by sending a cancel location.
HLR: Home Location Register is a mobile operator’s database in-home (HPLMN) network that controls the subscription of a mobile sim card. When a person gets a new sim card, the details are provisioned in HLR. The primary key for a subscriber in the database is IMSI and MSISDN. The dynamic information keeps updating in HLR.
When a sim card moves from one location to another or on a device, turn it on. The home network gets updates for visiting VLR/MSC. If a subscriber is allowed to roam, HLR sends subscriber data to VLR.
RNC(3G): Radio Network controller is a node between MSC and the access antenna. RNC node standardized in the 3G network.
NodeB: NodeB is in 3G. It has similar functionalities as BTS in the 2G network.
HLR lookup result parameters:
When an HLR lookup query for an MSISDN returns success, the result contains the following information.
- IMSI of subscriber
- Visiting MSC
- MCC and MNC of roaming network.
- Subscriber Status (Success/Failure).
- Number Portability Information Can be derived by looking at IMSI and MSISDN.
- The name of the mobile operator the current number belongs to.
When the outcome is a failure:
- Subscriber has not been configured for SMS Teleservice.
- The subscriber is not attached.
- Query Timeout.
- SMS service is barred.
- Protocol Level errors or provider errors.
Mobile Number Portability:
Switching to a new mobile operator without changing your phone number is known as mobile number portability. There were roaming charges within the same country in some places (for example, India). So, when someone moves from one location to another within the same country, they can use MNP with the same operator to avoid paying roaming fees.
A subscriber receives a new sim card as part of the porting process. To request number portability, you need to send an SMS to the original mobile operator for porting request from the original sim card. The entire procedure usually takes two to three days. The older sim card is deactivated after completion, and the newer one is activated.
What is the MNP database, and how useful for HLR lookup?
Every country has an MNP database (DB) that binds a mobile phone number to the appropriate service provider. It allows calls and SMS traffic to be routed to the correct destination. The database is accessible to all mobile operators. When an application requests an HLR lookup, the MNP DB is queried to obtain the serving HLR for the MSISDN.
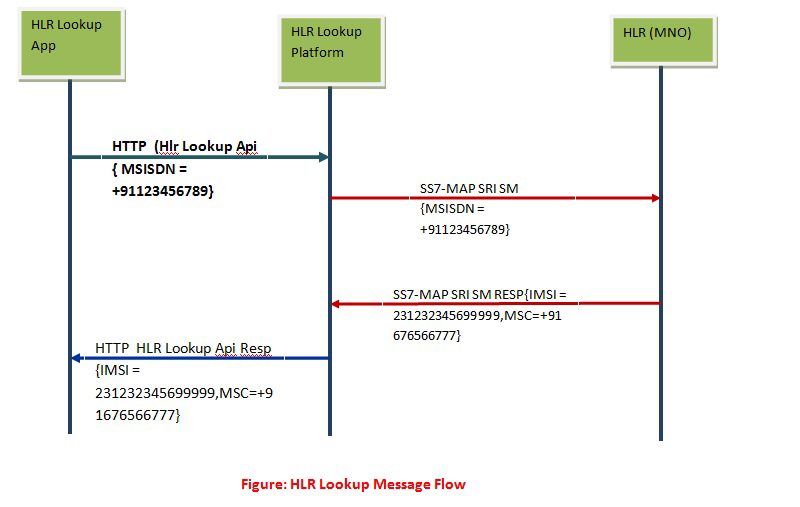
Call Flow for phone number lookup :
The ss7/Sigtran is the communication protocol between HLR and the lookup node/gateway. The originator initiates a GMS MAP 09.02 operation (SRI-SM) towards the HLR. The map operation has MSISDN as a mandatory key parameter.
When SRI-SM reaches the destination, the MSISDN lookup is performed in the database; if a subscriber is configured and the mobile phone is active/attached, IMSI and MSC number sends back to the lookup node in response.
The lookup node may have connectivity to all operators (according to coverage) directly or via an aggregator for ss7/Sigtran connections. Each node in the ss7 network is identified by a global title (digits) and a point code. Standard GSM bodies allocate both. Every mobile operator is given a range of global titles and IMSI ranges.
Mobile phone attached procedure:
When a mobile phone switches on, it does the following procedures to get access to the mobile network.
- Authentication, the mobile device sends the SendAuthenticationInformation operation from VLR to HLR over the SS7 network. Suppose a subscriber has been set up on HLR. VLR receives the authentication information response. The IMSI in the authentication request is the key.
- Update Location, VLR sends the update location operation over SS7 after successful authentication. The key parameters in the update location message are IMSI, VLR, and MSC. The HLR sends the subscription data (TeleService, GPRS data, Call Forwarding, Call Barring, and so on) to the VLR so that the mobile user can get the services they want. HLR updates the roaming VLR and MSC numbers in the local database after a successful location update.
In the HLR lookup response, the roaming MSC number is returned to the lookup node, which is received during the location update procedure.
Benefits from lookup:
- Least Cost Routing: The bulk SMS service provider receives the location information as a result of the lookup (visiting country and visiting network). SMS can be sent to a mobile subscriber via a low-cost route or network connection provider.
- Marketing database cleanup: When sending SMS to a mobile phone, the subscriber may or may not always be present. It costs money to send this subscriber message repeatedly, if not present, results in no return on investment. If the lookup fails, the HLR lookup service returns a status code for the subscriber. If an error results in a permanent failure (for example, Unknown Subscriber), the database for this subscriber can be cleaned.
- Billed the correct mobile operator. The mobile number portability information can be obtained from the lookup result. A lookup service provider can send CDRs to the right mobile operator for billing.
- Save costs by using a more cleaned, accurate mobile number database. A lookup service use can save costs. There are organizations, e.g., Colleges or Universities, that do very regular messaging to thousands of alum members. Lookup services clean the database for inactive numbers. The lookup saves thousands of dollars.
- Real-Time Information, HLR Lookup, provides real-time information for a roaming subscriber. This enables the service user to plan advertisements according to the roaming places.
- Used by VoIP providers, A VoIP provider, e.g., Skype, can make a lookup before terminating a call to the roaming device. The information collected can be used to set up a low-cost call route.
- Get if a number is mobile or landline. There are different formats for landline and mobile numbers in some countries. But in many, the format is the same. Just looking at digits can not say if a number is mobile or landline. Sending a text to a landline number has no use. HLR lookup provides information if a number belongs to a mobile or landline.
Location-based content marketing, These days, content marketing is vital and effective. Advertisers want to reach people who are close to the business premises. HLR lookup returns the current location of a mobile user. Content provider uses location information to advertise product effectively.
HLR Lookup service provider:
Companies are providing HLR lookup services. The lookup service can be accessed via API or from a Web interface. The service provider exposes HLR lookup APIs. The lookup service runs on a web domain or public IP. A service user can access a lookup server over the internet. To initiate a lookup API from software to the service platform. First, an account on the server should be created for a service user.
The service platform checks the details of a user using the HLR lookup API. If a user can use the service, the provider does an HLR lookup on the ss7 network and sends the result back to the service user. Sometimes an SDK is provided to the user for easy-to-develop lookup service applications.
Cell Id lookup:
The SMS service user always tries to get more and more accurate locations for a mobile phone. A simple HLR lookup provides the information for the roaming country and roaming area. The roaming area might be 20 kilometers wide. This gives some ideas for promoting location-based content but is still not useful when content marketing is based on a nearby location. E.g., sending restaurant information that is just 500 meters away from a mobile user. For that, a new parameter called cell id might be helpful.
Cell Id lookup maybe provide an additional parameter in the HLR lookup result. Cell id gives more accurate location information. On receiving a cell id lookup, HLR has to perform a cell id get operation with the VLR. VLR returns the LAC (location area code) and Cell (ID) along with MCC and MNC. The service provider can drive approx location coordinates from cell id and other parameters.
Cell Id lookup call flow:
SS7 MAP level, the lookup nodes send the ATI or Any Time Interrogation GSM MAP 09:02 operation to the HLR. HLR sends the PSI or Provides subscriber Info to the VLR. On success, the VLR sends the cell id in the response of PSI, and the cell id information, is relayed to the lookup node in the ATI response.
What is IMSI Lookup?
IMSI lookup is the process of getting IMSI using a mobile number. IMSI provides complete information about the mobile operator and subscriber. The next step for a lookup service provider should have access to the MCC and MNC databases. One can offer IMSI lookup service by using an HLR lookup service and access to the MCC and MNC databases.
HLR lookup service selection:
Once you have decided you need the lookup service, many HLR lookup service providers exist. Whom to choose? The following are the parameters that help you to decide to choose a service provider.
Coverage :
The most important thing is the coverage. E.g., if you want to provide your services to Indian mobile users, but if an HLR lookup provider does not have coverage in India, then do not choose this vendor.
Now have coverage in India, next, check if all mobile operators are covered within India, if not then check for other service providers.
Delivery Report :
The delivery report is very important for the end user. Check if the service provider conveys the correct error code in the lookup APIs response. This helps you to design your business logic more accurately.
Sigtran and HLR lookup:
Sigtran is ss7 Signalling over IP. Before the Sigtran, there were only ss7 links (E1 /T1) were available for HLR lookup. Links were deployed by the MNO to connect its infrastructure or premises. A service provider needs to put the box at the mobile network operator (MNO) premises for the service. This causes us to deploy at least one box for each MNO. Cause too much expense and results in costly service. With Sigtran, a service provider can set its HLR lookup box in his office and can connect to multiple MNOs from the same box. This reduces time and money. Sigtran uses SCTP protocol over IP.
VLR Lookup:
At the start, we have discussed what is VLR in telecom. Here we will discuss the VLR lookup. VLR lookup returns the roaming information. The roaming information is useful for routing ss7 Signalling in an optimization way. There are VLR lookup providers for the service. There are APIs that take input as MSISDN and return VLR information.
What is MCC MNC lookup?
In the above, we have mentioned the outcome of a lookup. From the result, MCC and MNC can be derived. Service providers use this information for number portability. For example, if a number has been ported. The service provider will use MCC and MNC to get the currently serving HLR global title.
Another option to get the serving HLR is the MNP database. The mobile operators connect to the portability ( MNP DB) database and get theHLR global title from a mobile number. The MCC and MNC lookup is useful for a service user who does not have access to the MNP DB.