What is a Private APN, and how does it secure a corporate network?
An Access Point Name (APN) is the address of a gateway located within the HPLMN of a Mobile Network Operator (MNO) that is used to provide Internet access to its subscribers. In a 3G network, it is known as GGSN. While in 4G, it’s PGW.
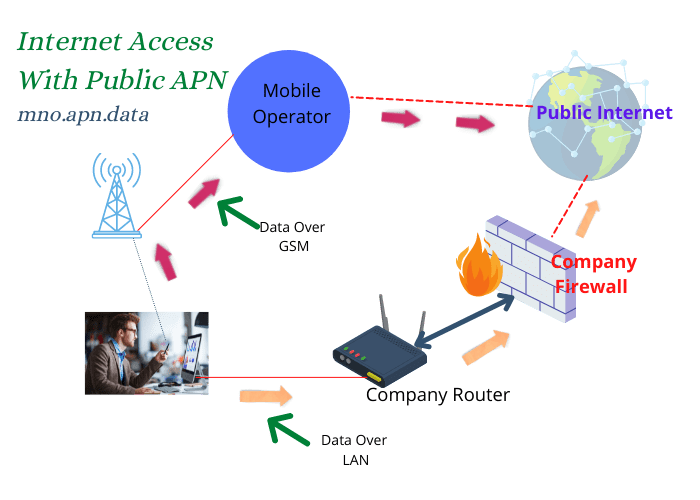
A mobile user is required to configure the APN name on the device in order to access the data services. Access Point Names (APNs), which are used by any SIM card from an operator, are public APNs.
SIM cards may have multiple access point names, each representing a gateway. A secure tunnel is set up towards the gateway when using a mobile phone to access the Internet.
An example would be when a web page request reaches the getaway, which forwards the request to the website hosting server over the public Internet, which is not a secure network.
Why a company needs a private APN?
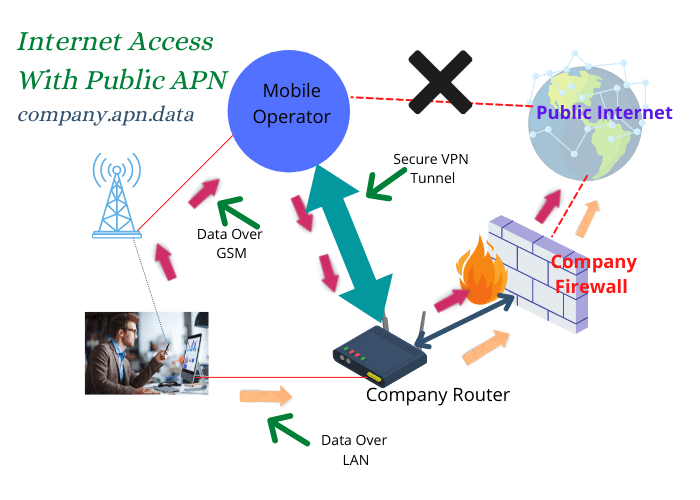
An APN that belongs to a company is known as a private APN. With a private APN, all mobile traffic that goes out from MNO to the Internet will first go to the network of the company over a secure tunnel (private APN user).
With a private APN, companies have control of all network traffic for mobile devices along with LAN.
For example, if all internet traffic goes out via a firewall from the local area network. But what if the same company also wants to pass all mobile data traffic via the same firewall? To do so, they need to get all internet traffic from MNO to their network.
Here comes the role of the private APN. When a device attaches to the network with private APNs. Through a secure VPN, the mobile operator routes all mobile internet traffic to the company’s network, where it is routed through a firewall toward the destination.
How a private APN works?
Following are technical points about internet traffic routing when using a private APN.
- A company sets up a firewall and all access points or a router within the office and sends all internet traffic via a firewall.
- The firewall applies the rules and sends the request to the server on the Internet. If it finds anything malicious or unauthorized, it drops.
- To secure the data communication from the cellular network, the company buys the private APN.
- To access the Internet, the devices in the company need to configure with a private APN.
- When mobile devices access the Internet, outgoing packets first reach the MNO. MNO checks network traffic from an APN belonging to the company. It sends the packets to the router over a secure VPN tunnel.
- A router routes packets to the external networks via the firewall, as they are coming directly from the LAN.
Why are Private APNs suitable for IoT and M2M devices?
An Internet Of Things (IoT) device accesses the Internet by using a SIM card. It sends the data read by the censers to a central server located somewhere over the Internet. Suppose the IoT device company needs to use a private APN to make communication secure and faster. The MNO will set up a tunnel with the server and route all device traffic to the server and vice versa.
M2M devices also need a similar secure network.