What is MSRN in GSM?
The full form of MSRN is a mobile subscriber roaming number. This is a 3GPP-specified E.164 type of number. A roaming network provides the called subscriber with a temporary identification, referred to as MSRN, for each incoming call.
A mobile network operator reserves a range of numbers for roaming subscribers from the range of MSISDNs. These are temporary numbers, and the network only allocates one number per call. Once the call completes, the number becomes usable again for another call.
This enables a subscriber to roam across the globe and keep connected. Discuss how a mobile terminated (MT) call works in the roaming scenario.
MT Call Flow with MSRN:
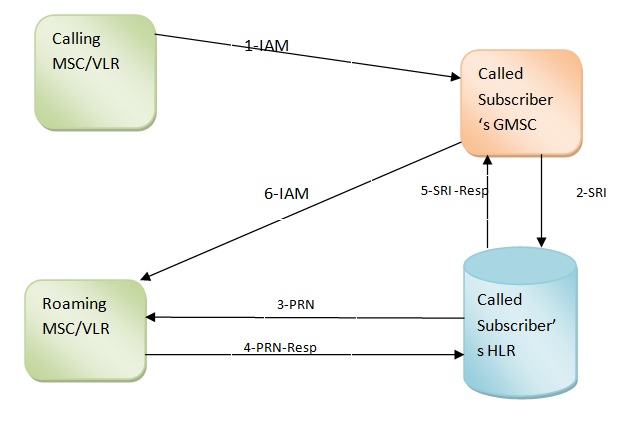
- When a subscriber dials a mobile number, the call reaches the GMSC of the called subscriber.
- The caller’s MSC starts ISUP signaling for the call setup by initiating an IAM message.
- Once GMSC receives the call (or IAM), it finds the subscriber’s status and roaming information (MSRN).
- GMSC sends the SRI (Send Routing Info) map protocol operation to the HLR to get the information.
The following describes the actions on HLR for MSRN.
- Upon getting SRI, HLR looks for the subscriber provisioning status. If a subscriber is not provisioned, HLR returns an error to the GMSC, and eventually, the call disconnects.
- Once an entry is found, it checks for the service status of the subscriber. Service status means if a subscriber is allowed for MT calls. If not, then the call disconnects.
- Next is the online status check. Online status means if a subscriber is attached to the network. If yes, HLR sends the Provide Roaming Number (PRN) map protocol operation to the visiting MSC/VLR. The roaming network returns the MSRN to the HLR if all is good. In turn, HLR sends the MSRN to the GMSC in SRI response.
- GMSC initiates a new IAM towards the MSC using MSRN as the called party. Now the phone rings, and calls get connected.
Why need an MSRN (a temporary number)?
As we mentioned earlier that MSRN is similar to a normal subscriber number. Then why do we need another number? Yes, the call can work without MSRN, but only if the subscriber is not roaming. The Telecom network does the routing based on county code and network code. What are the network and country codes you can find in the MSISDN tutorial on our blog? The country and network code combination changes if a subscriber roams in another mobile operator’s network.
With the help of MSRN, the mobile network can hide the actual subscriber for security reasons.