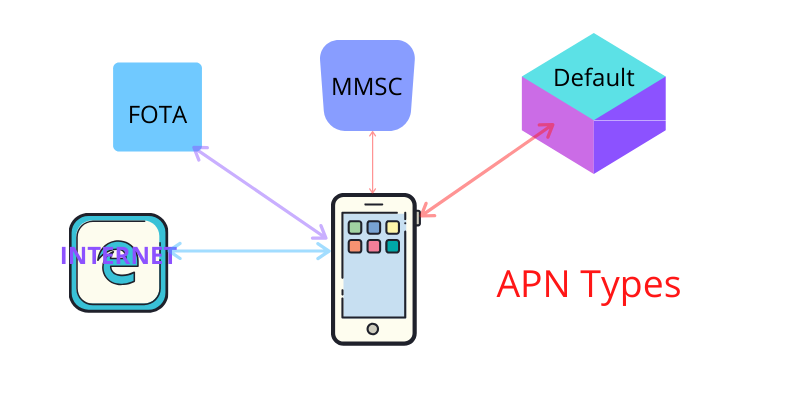
What is the APN type?
A SIM card needs to have GPRS settings to access the internet. The mobile operator sells the card with preloaded settings or updates over the air upon activation. APN and type are essential parameters in settings. The former is the address of the gateway to access the internet, and the APN type is for what kind of data connection will be, e.g., MMS, VPN, etc.
The configuration contains a wild card if there is a single APN for all types. In this tutorial, we will describe each type.
MMS Apn Type :
This type of APN represents the service gateway for MMS communication. When a SIM card tries to send and Multimedia message, the MMS type of APN is selected if there is any. For an MMS, additional parameters will be required to configure in the settings, e.g., MMSC, Proxy or Ports, etc. Here you can check How to do APN settings on the iPhone?
SUPL Apn Type:
The SUPL means for secure user plane location. SUPL location type APN set up a secure connection with the location server in the operator’s network. Most of the time, the default APN also serves the server for location.
Default Apn Type:
As the name implies, this is the APN used for all data connections for all types of requirements unless a different kind of APN is not set up explicitly. A mobile operator may have multiple APNs configured in HLR for a subscriber, out of which one is the default.
DUN Apn Type:
DUN is for Dial-Up Networking connections for the internet. Dial-up is the older method for an internet connection. So this APN type is not used.
FOTA Apn Type:
Firmware Over the Air, or FOTA, is the gateway for setting up a data connection for firmware updates. The default pan is used for Firmware updates too. But sometimes, there is a need for a separate connection for firmware updates only. Check APN settings on Android.